Bridge Circuits Instrument Information
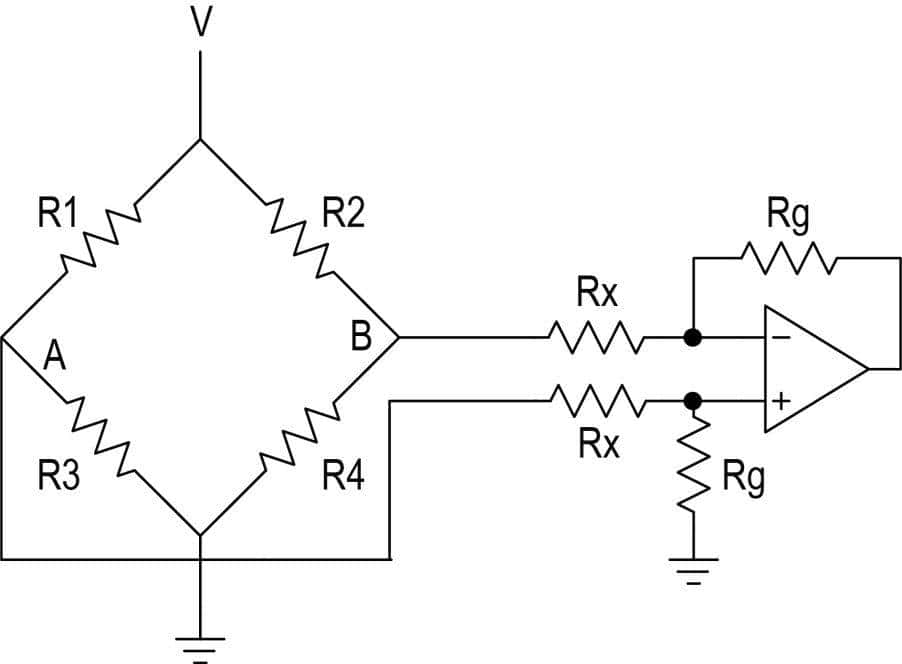
An electrical circuit in which two circuit branches (usually wired in parallel with each other) are bridged by a third branch. The most common type, a Wheatstone bridge, contains four resistors: two of known values, one which is variable and calibrated, and one whose resistance is to be determined. The circuit is subjected to power and hooked up to a galvanometer. The variable resistor is then changed until the galvanometer reads zero. It is then determined that the ratio between the variable resistor and its known neighbor is the same as the ratio between the unknown resistor and its known neighbor.
Common Uses
- Testing of electrical circuits for a number of different electrical characteristics
Common Types
- Wheatstone
- Wien
- Maxwell
- H
- Fontana
- Diode
- Kelvin
- Lattice
- Bridged T
- Carey Foster
Measurement Parameter
- Varies
Calibration Discipline
Calibration Equipment Used
- Decade Resistors