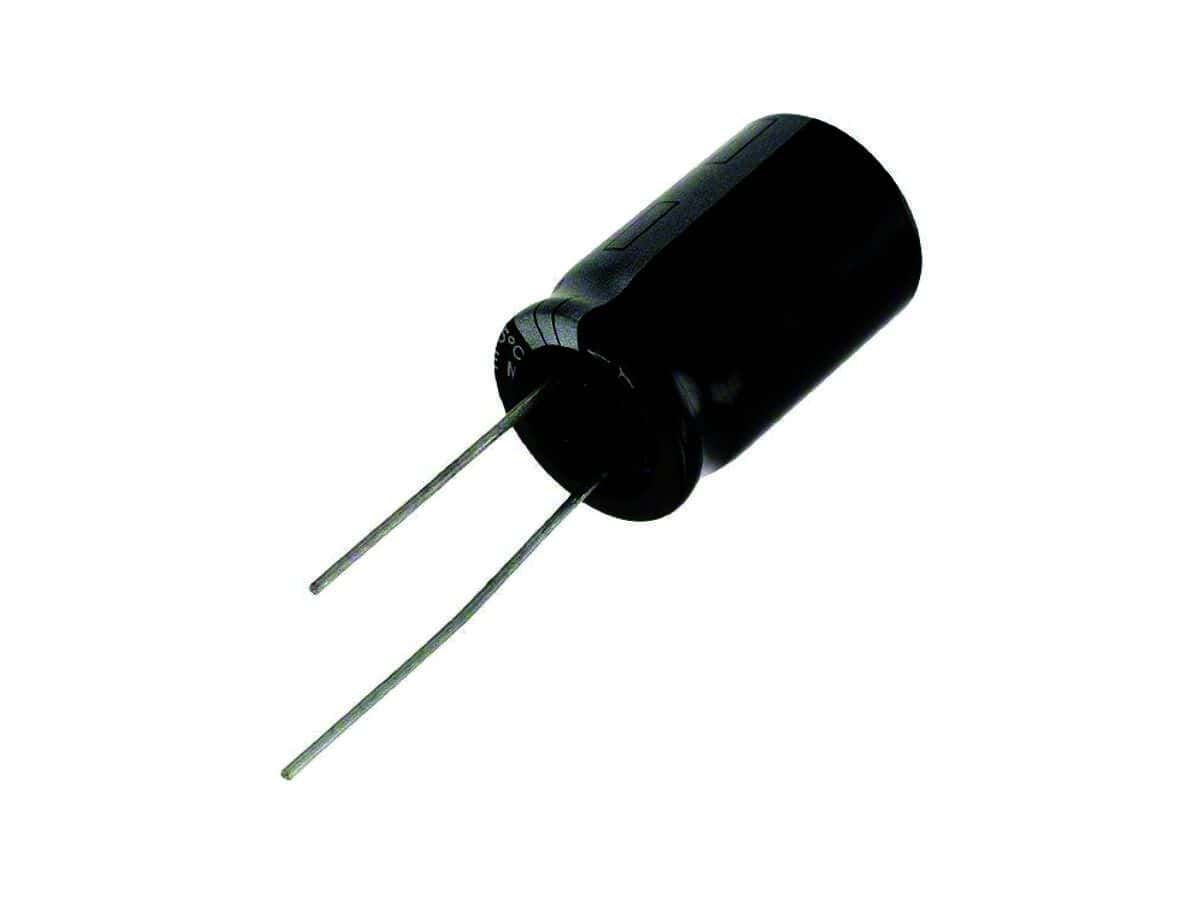
Capacitor Instrument Information
A passive, two-terminal electronic device which stores electrical energy. The capacitor consists of two conductors, often in the form of metallic plates, foil, thin film, bead of metal or electrolyte, separated by a dielectric medium, such as glass, ceramic, plastic, paper, or mica. When the two conductors experience a voltage difference, an electric field is created across the dielectric with a positive charge collecting on one conductor and a negative charge collecting on the other. This charge can then be manipulated or used at a later time.

Common Uses
- Storing energy in an electrical system, like a temporary battery, commonly in commercial electronic devices where a disconnect from electrical source would be damaging.
- Blocking DC signals but allowing AC signals to pass through an electrical system.
- Motor starters.
Common Types
- Fixed
- Polarized
- Variable
Measurement Parameter
- Capacitance
Calibration Discipline
Calibration Equipment Used
- LCR Meter
- Thermohygrometer